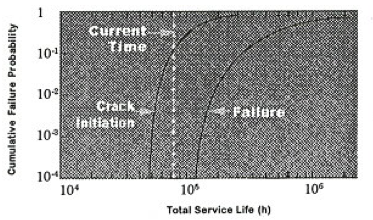
Creep damage is a time-dependent phenomenon characterized by gradual, continuous deformation, affecting all metals and alloys, under the combined action of temperature and stress. In general, creep damage accumulation and the propensity for rupture/failure is a function of material properties (including chemical composition, microstructure, heat treatment, strength, component geometry/ constraint, and previous loading history or deformations that may be present), operating stresses (whether load or displacement-controlled), metal temperatures, and time in service. High temperature creep damage accumulation over time can lead to void growth and crack formation, eventual rupture of pressure equipment, and failure of components and structures.
Equipment Susceptible to Creep Deformation
Fired heater tubes are distinctly prone to creep damage as they are often exposed to elevated temperatures for long periods of time. This includes other internal heater components such as tube supports, guides, and hangers. In the refining industry, hot-walled catalytic reformer piping, reactors, and associated components are prone to creep damage. Additionally, hydrogen reformer tubes/headers, FCC unit equipment such as hot-walled reactors, fractionators, and regenerator internals are susceptible. In general, if internal refractory degradation occurs on cold-walled equipment (e.g., FCC reactors), the related hotspot region can be prone to either short-term overheating or long-term creep, if not properly remediated. Low creep ductility failures have occurred in weld heat-affected zones (HAZ) at nozzles and other highly stressed areas on catalytic reformer reactors and piping components. Creep-related cracking has also been observed at longitudinal seam welds in high-temperature piping. Also, welds joining dissimilar materials (i.e., ferritic to austenitic welds) may suffer creep related damage at high temperatures, partially due to differential thermal expansion stresses.
In the power generation industry, high-temperature superheater and reheater tubes and high-pressure steam generation components such as fired boilers, piping systems/headers, steam drums, and related equipment are subject to long-term creep damage. In other industries, creep can also affect many different components. For example, in the petrochemical industry, acrylonitrile reactors and ethylene cracker components can be degraded by long-term creep damage. In general, welded regions in any high-temperature equipment, areas that contain geometric discontinuities (e.g., thickness transitions, structural attachment locations, nozzle-to-shell junctions, etc.), and any area that is subject to the hottest operating metal temperatures should be prioritized for focused inspection for creep damage.
Three damage mechanisms that can reduce the creep resistance and creep ductility of certain steels are carburization, graphitization, and spheroidization. It is important to understand these three damage mechanisms when evaluating creep damage susceptibility and estimating remaining life because any of these mechanisms, under the right conditions, can dramatically reduce creep resistance and lead to accelerated creep cracking/damage accumulation and ultimately, failure.
Creep Detection
Inspection for creep damage is not straight-forward and it may require a combination of surface and volumetric non-destructive examination (NDE) such as visual inspection (VT), ultrasonic testing (UT), radiography (RT), and eddy current (ECT) to identify creep damage. Destructive sampling and subsequent metallographic examination/laboratory analysis are also useful tools to confirm the presence of creep damage or to carry out a failure analysis.
For pressure equipment, inspection should focus on welds, in general, but especially on Cr-Mo welds operating in the creep range. Welds may also contain original fabrication defects, lack of fusion, porosity, slag inclusions, etc., that often serve as damage initiation sites. Furthermore, the mismatch in material properties between weld deposits, heat affected zones, and adjacent base metal can increase the propensity for crack initiation and accelerate creep crack propagation. Considering 1-Cr 1/2-Mo and 1-1/4-Cr 1/2-Mo materials are particularly predisposed to low creep ductility, careful attention should be given to welded regions in these components. Commonly, inspections are performed visually and followed by periodic surface inspection methods such as wet fluorescent magnetic particle testing (WFMT) or liquid penetrant testing (PT) – note that surface inspection will not identify embedded damage. Angled beam (e.g., shear wave, phased array, etc.) UT techniques can be utilized as well, but early stages of creep damage are often difficult to detect and accurately characterize.
Creep Mitigation
A thorough damage mechanism review (DMR) and understanding of high-temperature material properties (e.g., allowable stresses and creep rupture data), welding parameters, heat treatment procedures, advanced mechanical design and fitness-for-service (FFS) techniques, inspection methods, creep testing protocols, and optimal process conditions can help guide the installation of robust equipment configurations and mitigate creep damage accumulation and creep cracking in common pressure equipment. Optimization of all these different parameters coupled with specifying supplemental design details and fabrication practices, often beyond construction Code-minimum requirements, represents the best approach for mitigating creep damage.
Related Topics
- Brittle Fracture
- Carburization
- Cavitation
- CO2 Corrosion
- Cooling Water Corrosion
- Corrosion Fatigue
- Corrosion Under Insulation (CUI)
- Cracking
- Decarburization
- Embrittlement
- Erosion Corrosion
- Fatigue (Material)
- Flue Gas Dew Point Corrosion
- Graphitization
- Green Rot
- High Temperature Hydrogen Attack (HTHA)
- Hydrochloric (HCl) Acid Corrosion
- Hydrofluoric (HF) Acid Corrosion
- Hydrogen Embrittlement
- Hydrogen Stress Cracking
- Liquid Metal Embrittlement (LME)
- Metal Dusting
- Microbiologically Influenced Corrosion (MIC)
- Naphthenic Acid Corrosion (NAC)
- Phosphoric Acid Corrosion
- Pitting Corrosion
- Spheroidization (Softening)
- Stress Assisted Corrosion
- Sulfidation Corrosion
- Sulfuric Acid Corrosion
- Thermal Fatigue
- Vibration-Induced Fatigue
- Wet H2S Damage
Relevant Links
Topic Tools
Share this Topic
Contribute to Definition
We welcome updates to this Integripedia definition from the Inspectioneering community. Click the link below to submit any recommended changes for Inspectioneering's team of editors to review.
Contribute to Definition