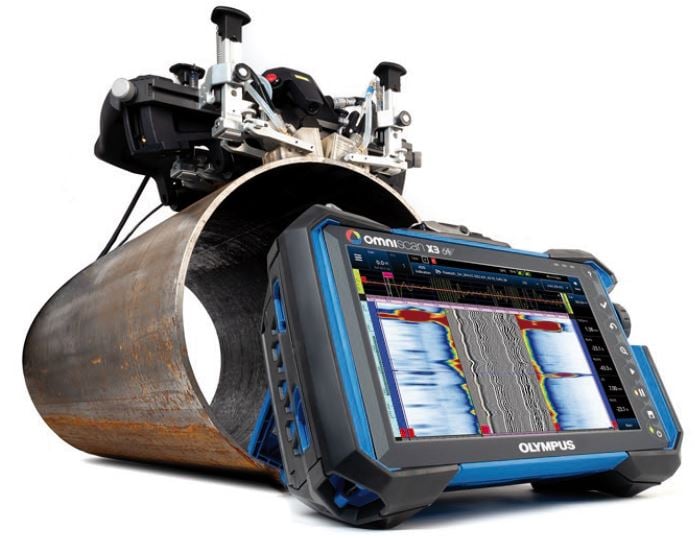
A Boiler is a piece of equipment which acts as a closed vessel to convert the water inside into steam. In order for this to happen chemical energy from a fuel source such as oil or gas is converted into heat by combustion. The heat is then transferred to the contained water, thereby increasing the pressure and eventually converting the liquid form into steam.
Boilers are one of the most fundamental systems of a refinery or chemical processing plant. They are literally the pieces of equipment that keep the plant up and running. Most industrial boilers fall into two broad categories of boiler types: Fire-Tube Boilers and Water-Tube Boilers. In fire-tube boilers, hot gas passes through one or many tubes, which through thermal conduction, heats the water surrounding them. In water-tube boilers, water circulates inside the tubes and is heated externally by hot gases generated by the furnace.
Related Topics
- Aboveground Storage Tanks (ASTs)
- Boiler Tubes
- Bolts
- Coker Units
- Cooling Towers
- Crude Distillation Unit (CDU)
- Deaerators
- Fired Heaters
- Fixed Equipment
- Flanges
- Flare Systems
- Furnace Tubes
- Glass-lined Equipment
- Heat Exchangers
- HF Alkylation Units
- Hydrocracking Unit
- Hydrotreater
- Piping
- Pressure Relieving Devices (PRDs)
- Pressure Vessels
- Rotating Equipment
- Vacuum Distillation Unit (VDU)
- Valves
Relevant Links
Topic Tools
Share this Topic
Contribute to Definition
We welcome updates to this Integripedia definition from the Inspectioneering community. Click the link below to submit any recommended changes for Inspectioneering's team of editors to review.
Contribute to Definition