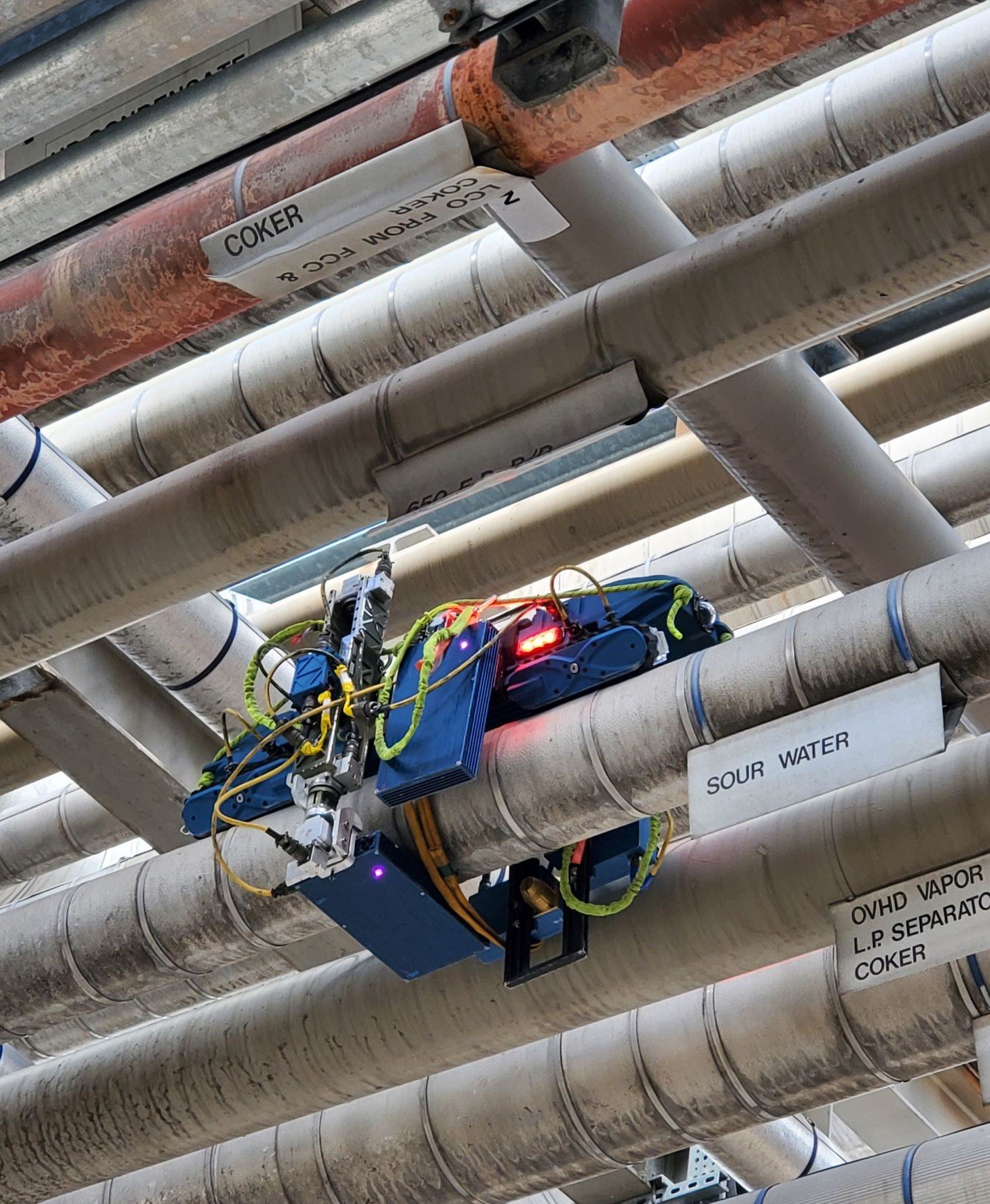
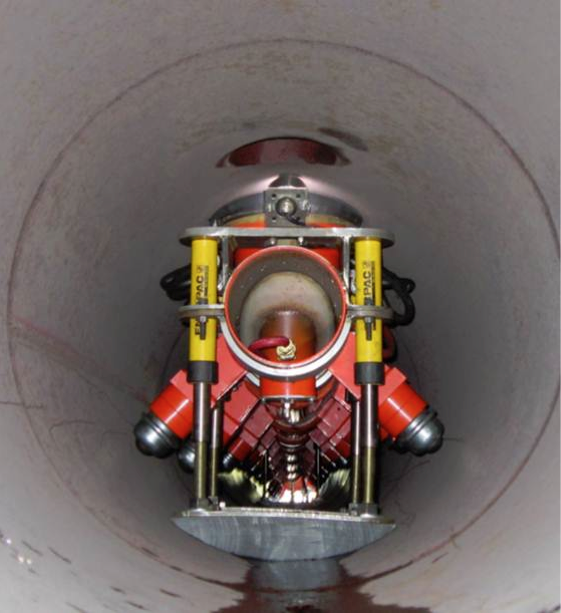
Fired Heaters, often referred to as furnaces (direct fired heaters), are pieces of equipment often used in processing facilities to heat gases or liquids up to a desired temperature. Fired heaters in the petrochemical and refining industry are critical pieces of equipment that can have a major impact on process unit safety, reliability, and economics. They are complex pieces of equipment, where tubes and other pressure boundary components might fail due to relatively short periods of upset conditions.
Fired heaters come in two configurations: direct fired heaters and indirect fired heaters. Direct fired heaters utilize a burner to produce hot gasses that transfer their heat energy to a process liquid or gas flowing directly through furnace tubes installed inside the vessel. Indirect fired heaters utilize burners to heat a heat exchanger, over which cool air is circulated and heated.
The construction and design of fired heaters are governed by the API STD 560 or ISO 13705 standards. Their inspection is covered by API RP 573.
Related Topics
- Aboveground Storage Tanks (ASTs)
- Boiler Tubes
- Boilers
- Bolts
- Coker Units
- Cooling Towers
- Crude Distillation Unit (CDU)
- Deaerators
- Fixed Equipment
- Flanges
- Flare Systems
- Furnace Tubes
- Glass-lined Equipment
- Heat Exchangers
- HF Alkylation Units
- Hydrocracking Unit
- Hydrotreater
- Piping
- Pressure Relieving Devices (PRDs)
- Pressure Vessels
- Rotating Equipment
- Vacuum Distillation Unit (VDU)
- Valves
Relevant Links
Topic Tools
Share this Topic
Contribute to Definition
We welcome updates to this Integripedia definition from the Inspectioneering community. Click the link below to submit any recommended changes for Inspectioneering's team of editors to review.
Contribute to Definition