Ana Benz: About the Author
Chief Engineer, IRISNDT

Ana Benz, IRISNDT’s Chief Engineer, has worked for IRISNDT for 26 years as a Corrosion, Failure, and Inspection Specialist. Ana worked extensively for Chemical, Petrochemical Plants, Fertilizer Plants, oil and gas, and refineries. She is a University Simon Bolivar Materials Engineer graduate and obtained a Master’s degree in Materials Engineering from the University of British Columbia. She has a CGSB NDT certificate and CWB Level 3 and API 510 certifications. Ana was a member of the NACE Edmonton Executive and the Edmonton Chapter of the Canadian Welding Institute. She is also an IPEIA Special Sessions Committee member.
Is this you? Please help us keep this page up-to-date by occasionally submitting your updated information.
Published Articles
Software advances in laser scanning allow for examining noncylindrical equipment common in a plant environment. We’ll give six examples of how this is done.
This article illustrates the value of digital radiography as an efficient tool to visualize corrosion and other small bore piping anomalies without disturbing insulation, as well as using PRT in conjunction with UTT to survey small diameter lines.
Field hardness tests can provide valuable information when evaluating piping and pressure vessel anomalies. This article summarizes laboratory examinations designed to gain a better understanding of UCI hardness test results taken in the field.
Tanks are ubiquitous and essential in industrial societies. When they fail, the consequences can be dire if products/volumes they store are explosive and/or toxic.
The challenge to find CUI is difficult and one single NDE technique cannot be used to identify it. This remains the case today as we combine NDE techniques to perform CUI assessments. The techniques and strategies commonly used today are summarized in this article.
This article provides a discussion of a recent inspection performed at a U.S. refinery. Industry HF lines are experiencing piping failures in increasing numbers due to the presence of residual elements entrained within their carbon steel components.
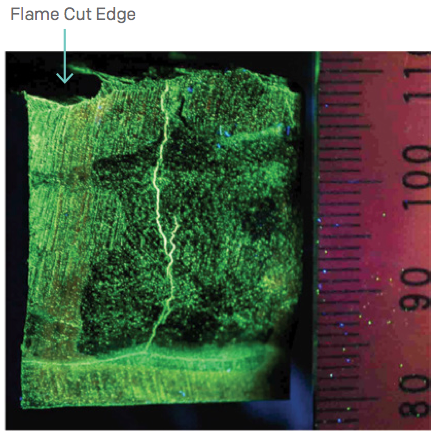
A small leak from top tubesheet-to-tube welds prompted further inspection of the 1¼Cr- ½Mo Ammonia Converter Boiler Feed Water (BFW) Exchanger during a planned shutdown. Further cracks were identified in the top channel to tubesheet butt weld that operated at 700 °F.
In this article you will find the failure investigations of six 0.094 inch thick carbon steel vessels. These vessels were in service in natural gas well facilities; some functioned as dryers and were subjected to cyclic loads. Metallographic tests, hardness tests, and fracture surface scanning electron microscopy (SEM) examination results are presented for each of the vessels.