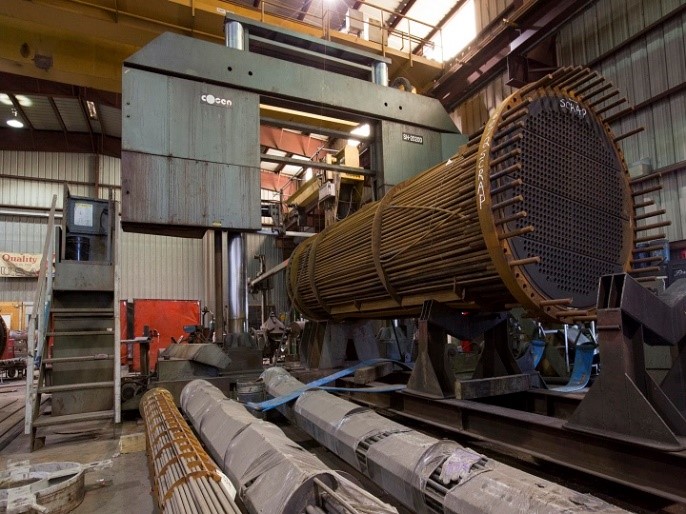
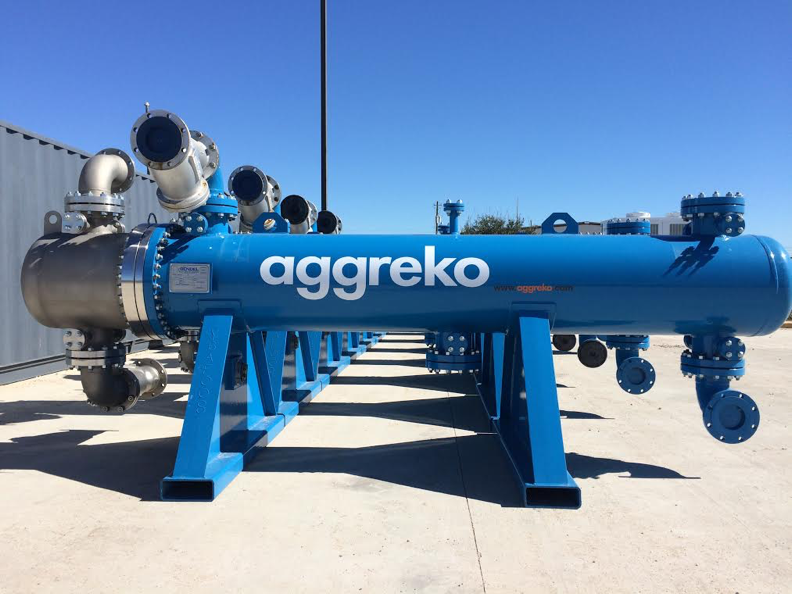
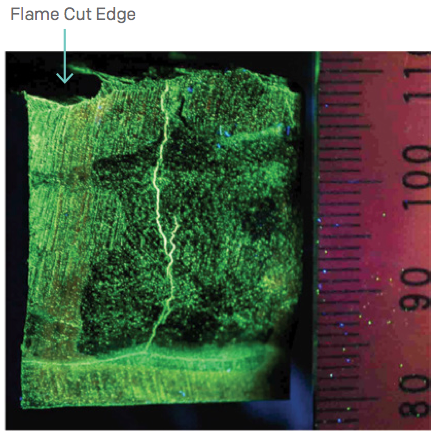
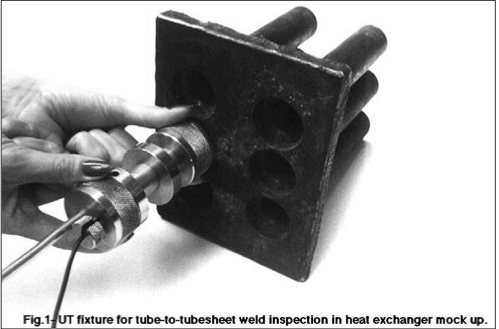
Heat Exchangers are pieces of process equipment built and designed for maximum efficiency of heat transfer between two different machines or mediums. In most industrial processes, the loss of heat is very wasteful and inefficient. Because of this, heat exchangers were created to capture and reuse heat that would otherwise be lost to the environment.
In general, a heat exchanger functions by allowing a hot fluid to flow through the exchanger past a cold fluid without intermixing the two. Heat flows from the hot fluid to the cold fluid, heating the cold fluid and cooling the hot fluid. This allows the heat to be transported and reused rather than simply discarded. The two fluids will flow past each other, with one usually being in a narrow pipe while the other flows outside the pipe in a surrounding shell.
There many different types of heat exchangers; some more appropriate for certain environments than others. Some have built-in dividers to separate the heat storage, while others allow the mixing of heat. Of these different types, each one fits into one of three larger classifications depending on its type of flow.
- Parallel-flow Exchangers involve two different fluids entering the exchanger from the same end and flowing in the same direction.
- Counter-flow Exchangers push the cold fluid from one direction of the exchanger while the hot will enter from the other direction and they will flow past each other. Counter-flow exchangers are often considered the most efficient at transferring heat.
- Cross-flow Exchangers push the hot and cold fluids in a perpendicular flow and exchanging heat at the intersection where they meet.
In the oil and gas and chemical processing industries, inspection and maintenance responsibilities for heat exchangers are often grouped in with other fixed equipment.
Related Topics
- Aboveground Storage Tanks (ASTs)
- Boiler Tubes
- Boilers
- Bolts
- Coker Units
- Cooling Towers
- Crude Distillation Unit (CDU)
- Deaerators
- Fired Heaters
- Fixed Equipment
- Flanges
- Flare Systems
- Furnace Tubes
- Glass-lined Equipment
- HF Alkylation Units
- Hydrocracking Unit
- Hydrotreater
- Piping
- Pressure Relieving Devices (PRDs)
- Pressure Vessels
- Rotating Equipment
- Vacuum Distillation Unit (VDU)
- Valves
Relevant Links
Topic Tools
Share this Topic
Contribute to Definition
We welcome updates to this Integripedia definition from the Inspectioneering community. Click the link below to submit any recommended changes for Inspectioneering's team of editors to review.
Contribute to Definition