Introduction
Industrial furnaces are used extensively throughout the entire oil and gas industry, as well as other process industries such as pulp and paper, metals and mining, chemical, and petrochemical. An industrial furnace, or direct fired heater, is a piece of equipment used to provide heat for processing or can serve as a reactor which provides heat for the reaction. Furnace designs vary as to their function, heating duty, type of fuel, and method of introducing combustion air. However, most process furnaces have some common features.
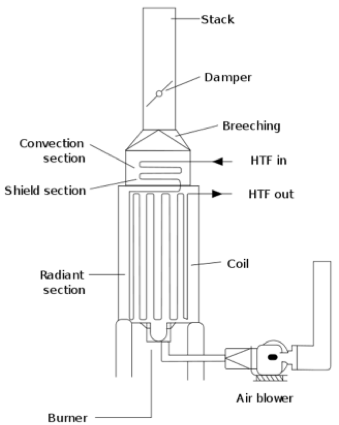
Fuel flows into the burner and is burnt with air provided from an air blower. The flames heat up the tubes, which in turn heat the fluid inside in the first part of the furnace (known as the radiant section), where the fluid reaches the desired process temperature. After that, the flue gas (gases from combustion) vacates the radiant section and enters the convection zone, where the heat is recovered before venting to the atmosphere. Figure 1 shows a typical gas heater.

















Comments and Discussion
There are no comments yet.
Add a Comment
Please log in or register to participate in comments and discussions.