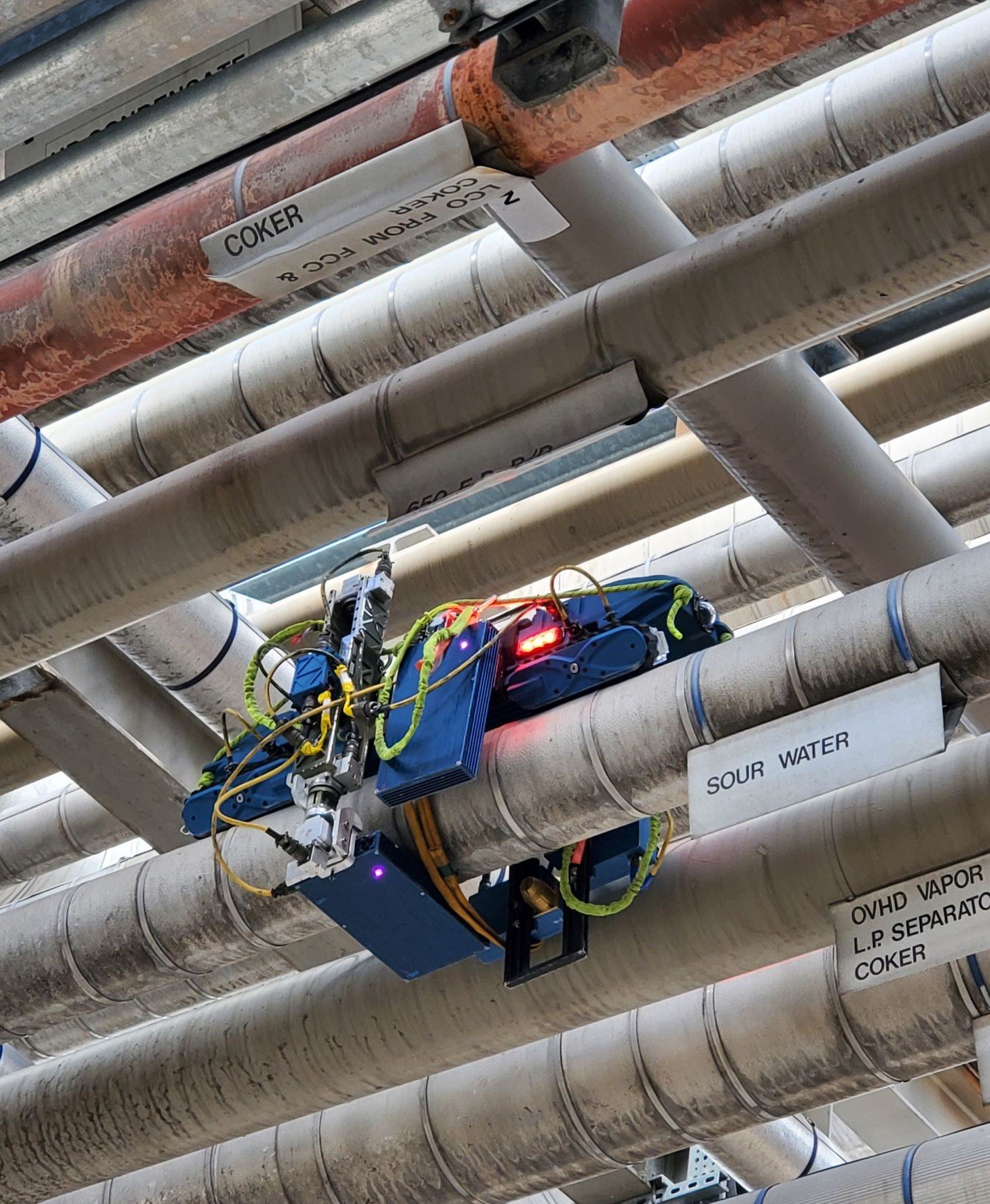
Condition Monitoring Locations (CMLs) are designated locations on pressure vessels and piping where thickness monitoring is conducted to monitor the presence and rate of damage and corrosion.
Most CMLs consist of at least one examination point, usually a two to three-inch diameter circle on the surface of the equipment. It’s within these circles that the inspection takes place. The number of specific spots where individual readings are taken within these areas varies. API 510 and API 570 recommend recording either the lowest or an average of several readings within the area of the examination point.2,3
The number and location of CMLs need to be a sampling that covers the entire population range. Additionally, the number is based on the user’s desired confidence in the sample data. In other words, more CMLs will produce more sample data, which, in turn, should increase a user’s confidence in the estimated condition. More locations should be used to monitor higher risk equipment. For sites that have implemented risk-based inspection, the number of CMLs will typically depend on the desired level of risk mitigation.
A Note on Thickness Monitoring Locations (TMLs)
Prior to the 9th edition of API 510 and 3rd edition of API 570, a thickness measurement location (TML) referred to a single examination point where thickness measurements would be performed in order to establish general and localized corrosion rates. Whereas a CML can include one or more of these points, CMLs now include what were previously referred to as TMLs. Upon publication of the 9th edition of API 510 and 3rd edition of API 570, API codes no longer use the designation TML independent of CML.
References
- Gysbers, A.C., 2012, “A Discussion on the Piping Thickness Management Process: Determining Corrosion Monitoring Locations,” Inspectioneering Journal, 18(6), pp. 6-11.
- API 510 — Pressure Vessel Inspection Code: In-Service Inspection, Rating, Repair, and Alteration, The American Petroleum Institute, ed. 9, 2006.
- API 570 — Piping Inspection Code: In-service Inspection, Rating, Repair, and Alteration of Piping Systems, The American Petroleum Institute, ed. 3, 2009.
Related Topics
- Cathodic Protection
- Coatings
- Corrosion Control Documents (CCDs)
- Damage Mechanisms
- Positive Material Identification (PMI)
Relevant Links
Topic Tools
Share this Topic
Contribute to Definition
We welcome updates to this Integripedia definition from the Inspectioneering community. Click the link below to submit any recommended changes for Inspectioneering's team of editors to review.
Contribute to Definition